Introduction
“A healthy smile begins with what’s on the plate.” Described as a “silent epidemic,” Poor oral health affects nearly 4 billion people globally, with more than 530 million of them being children. This condition leads to considerable economic losses, with untreated dental caries (cavities) being the leading health issue worldwide, as stated by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Oral health is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) “as being free of chronic mouth and facial pain, oral and throat cancer, oral sores, birth defects such as cleft lip and palate, periodontal (gum) disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss, and other diseases and disorders that affect the mouth and oral cavity”. Nowadays, dental caries and periodontal diseases are two of the most prevalent diseases worldwide, and simultaneously, easily preventable with simple primary prevention methods. They are the main cause of dental loss and therefore are considered as an important public health issue that affects children, adolescents, adults and the elderly. The Lancet reports that permanent dental caries are the most prevalent among 328 major diseases worldwide.
Dental caries is a common disease in children that causes pain with a resultant effect on various physiological and social functions Dental health is closely related to the quality of life, including demographic factors, psychological factors, oral hygiene management, oral health behavioral factors, and socioeconomic factors. The role of teeth in oral health is crucial and demands attention, with continuous care needed to prevent oral diseases. In Africa, poor oral hygiene and high sugar intake contribute to the increasing burden of dental diseases, worsened by limited access to dental care.
In Kenya, many school-aged children suffer from cavities due to diets high in processed sugars and poor oral hygiene practices. The first (and only) Kenya National Oral Health Survey in 2015 reported a high oral disease burden. Notably, the prevalence of dental caries in children is 40%, gum disease is over 90%, and dental fluorosis is 41%. This population is disadvantaged for several reasons, and many factors influence their quality of life, including food and nutrition, inadequate access to healthcare services, lack of proper oral hygiene habits, and non-intercepted harmful oral habits, but also predisposition related to the ethnic group. Both public and private institutions provide oral health care services. A greater proportion of oral health care providers work in urban centers, making oral health care services difficult to access for the majority of the Kenyan population. The provision of basic oral healthcare is capital intensive. This translates to a high cost in the provision of oral health care. There is a need for quality oral health care that is affordable, accessible, and acceptable.
In counties like Homabay, economic constraints, and dietary habits significantly affect children’s health. Poor oral health can adversely impact children’s performance in school, and later, it may affect their self-esteem and accomplishments in life. In addition, children with poorer oral health are more likely to suffer dental pain, miss school, and show underperformance in school. Many schools lack proper awareness programs on oral hygiene and nutrition, making it crucial to educate pupils on the impact of diet on dental health.
The Link Between Nutrition and Oral Health
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining strong teeth and gums. The foods and beverages children consume play a vital role in their oral health. Inadequate intake of micro-nutrients such as vitamins, folate, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium, may result in micro-nutrient deficiencies, which compromise the structure of children’s teeth and thus result in dental caries. Excessive sugar intake also fuels the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to tooth decay, plaque buildup, cavities, and gum disease. Sugary snacks, carbonated drinks, and processed foods contribute to enamel erosion and dental caries. In contrast, a balanced diet rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D helps in enamel formation and maintenance and also strengthens teeth and gums, reducing the risk of oral health issues. Encouraging pupils to adopt sugar-free diets can significantly lower their chances of developing cavities and other dental complications.
Educating Pupils on Sugar-Free Diets
A sugar-free diet entails consuming whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and dairy while minimizing processed sugars found in sweets, sodas, and pastries. Encouraging water consumption and limiting acidic beverages also helps in maintaining a healthy oral pH balance, reducing the risk of tooth decay. Educating children about the dangers of excessive sugar intake and the benefits of nutritious foods is crucial in fostering lifelong oral hygiene habits. Schools should integrate lessons on:
- The effects of sugar on teeth and overall health.
- The importance of a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, dairy, and whole grains.
- Practical tips for reducing sugar consumption, such as choosing water over sugary drinks and opting for healthy snacks like nuts and fruits.
TajiZuri’s Role in Promoting Oral Hygiene
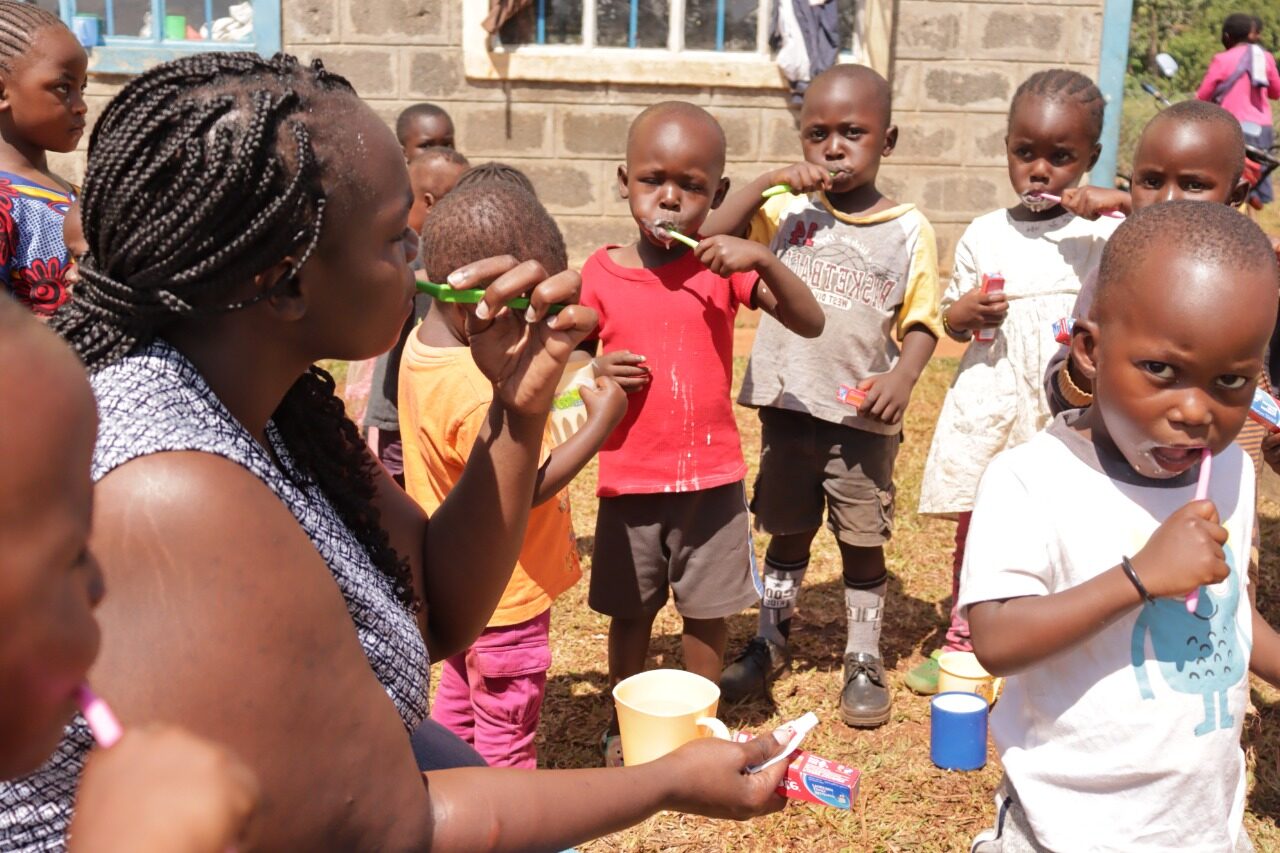
School is an important platform for learning. It not only contributes to an individual’s education but also to their health and health-related behavior. Recognizing the need for improved oral and nutritional hygiene among pupils, TajiZuri has implemented programs that empower students with essential knowledge and resources. Through interactive school sessions, pupils learn proper brushing techniques, the importance of flossing, and the dangers of excessive sugar consumption. TajiZuri collaborates with dental professionals who conduct routine screenings and offer preventive care to curb dental issues at an early stage. Through the Smile for Life program, we equip pupils with the tools and education needed to maintain good oral hygiene. Through this program, students receive:
- A toothbrush to encourage daily brushing.
- A tooth brushing guide to help them develop proper brushing techniques.
- Toothpaste enriched with fluoride to strengthen their teeth.
- An educational flier that highlights the importance of oral health and proper nutrition.
By integrating these resources into school curricula, Smile for Life ensures that pupils build healthy habits early, reducing the prevalence of dental issues eventually.
Lishe Bora Program
According to the World Food Program (WFP), data from 163 countries show that 99% of these countries, including developed and developing countries, delivered school feeding programs (WFP, 2020). Studies strongly suggest that 90 percent of those meals were complemented by a package of interventions to improve health. Globally, one in every two schoolchildren, or 388 million children, received a school meal, although there were wide disparities between countries and even wider disparities resulted due to the pandemic (WFP, 2020).
School meal programs address objectives related to health and nutrition by reducing hunger and improving children’s micro-nutrient status with diverse menus and food fortification; particularly in Homabay schools. Beyond oral hygiene, TajiZuri also focuses on promoting proper nutrition through its Lishe Bora program. This initiative educates pupils on:
- The impact of nutrition on overall health, including oral health.
- How to identify and consume nutrient-rich foods that support strong teeth and gums.
- The dangers of excessive sugar intake and how to make healthier dietary choices.
The Lishe Bora Program integrates nutrition education with practical interventions to promote healthy eating habits. Pupils are introduced to sugar-free meal plans, with an emphasis on nutritious, affordable, and locally available foods. The program also involves school feeding initiatives prioritizing balanced diets rich in essential vitamins and minerals, supporting oral and overall health.
Through these initiatives, TajiZuri empowers pupils with knowledge and resources to make healthier dietary choices, ultimately reducing the incidence of tooth decay and promoting lifelong oral health.
Conclusion
Good nutrition and oral health go hand in hand. Recognizing oral hygiene as a vital subject, teachers advocate for more frequent instruction, noting the Colgate learning kit as a beneficial educational tool. By educating pupils on the importance of sugar-free diets and equipping them with the necessary tools and knowledge, we can significantly reduce oral health problems among children. TajiZuri’s Smile for Life and Lishe Bora programs play a crucial role in fostering a generation that understands the value of proper nutrition and oral hygiene. Through continuous education and community support, we can ensure that every child enjoys a healthy, confident smile for life. Continued collaboration between schools, healthcare professionals, and organizations is essential in sustaining these efforts and achieving long-term positive outcomes.
Article written by:
Sabwili Mpoyana
Nutrition Associate.